Double Asteroid Redirection Test ( DART)
About Double Asteroid Redirection Test ( DART)
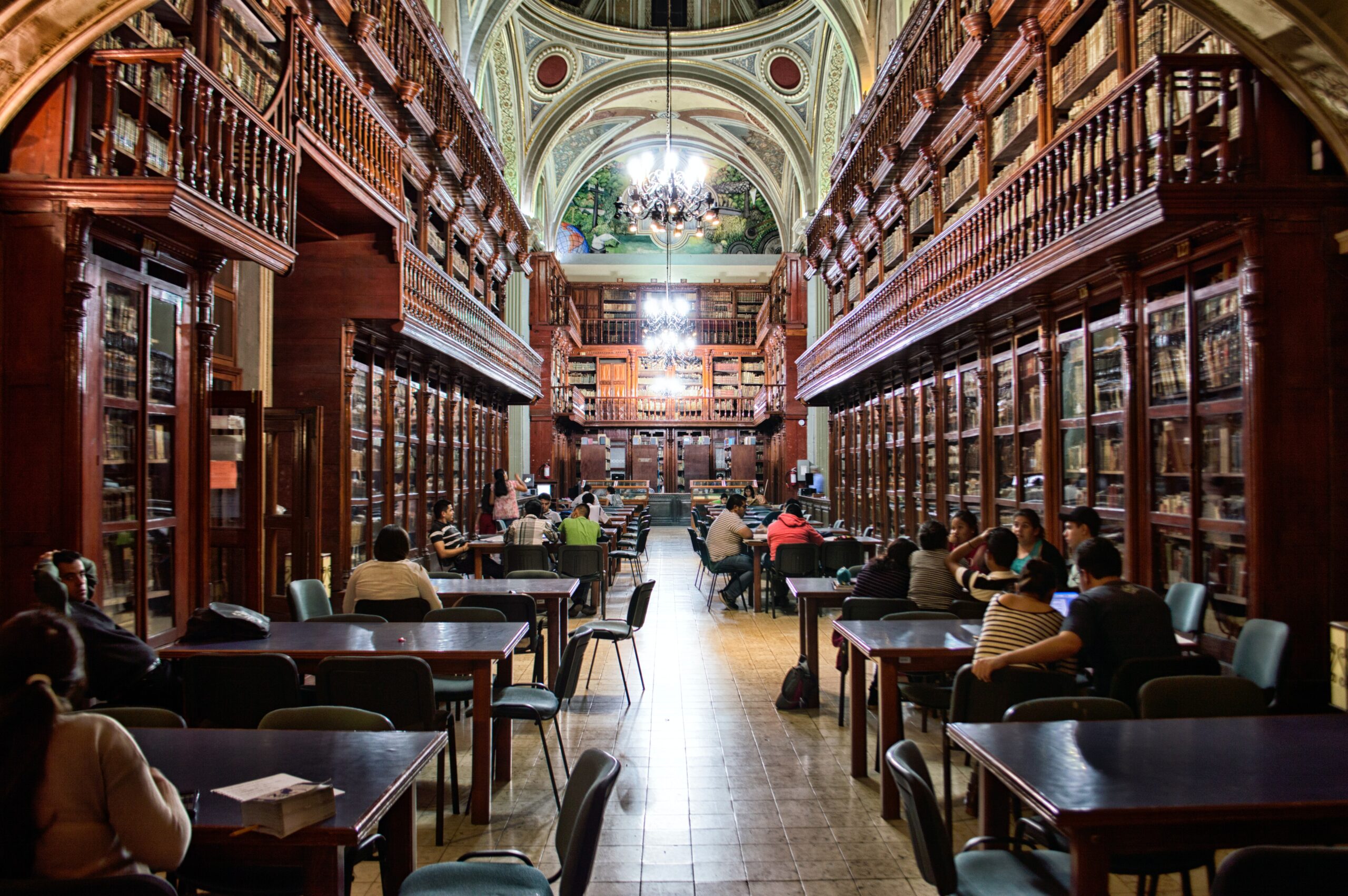
- DART is the world’s first planetary defence technology demonstration that aims to protect the planets from any possible collision with alien particles. This joint mission was carried out by NASA and John Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL). It was launched on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket.
- The DART carried a high-resolution DRACO (Didymos Reconnaissance and Asteroid Camera for Optical navigation) camera to observe the collision and its consequences. DRACO will be used for sending the image to the earth on a real-time basis. It will help in studying the object with precision.
- DART’s impact with the asteroid Dimorphos (explained later) demonstrates a viable mitigation technique for protecting the planet from an Earth bound asteroid or comet.
- Telescopes placed on the Earth’s surface will track the success made by this mission in changing the course of the asteroid.
- It will be a low-cost spacecraft. It has two solar arrays which uses hydrazine propellant for channelling spacecraft.
- Apart from DRACO, it will also carry a small satellite, CUBESAT called LICIAcube, which will capture the image of a crater formed as a result of the collision.
- The mission is part of NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office, which is responsible for identifying and tracking potentially hazardous asteroids and comets, and developing strategies to mitigate their impact on Earth.
- On 26 September 2022, the probe—which had been launched from Earth on 24 November 2021—intentionally collided with the moon of the minor planet Dimorphos, an asteroid named Didymos. On October 11, NASA announced that DART had succeeded in cutting Dimorphos’ orbital period around Didymos by around 32 minutes, exceeding the 73-second success requirement.
Objectives of DART mission
- The mission is to test the new technology to be prepared in case an asteroid heads towards the Earth in future.
- The aim is to test the newly developed technology that would allow a spacecraft to crash into an asteroid and change its course.
- The target of the spacecraft is a small moonlet called Dimorphos (Greek for ‘two forms’).
- Dimorphos orbits a larger asteroid named Didymos ( Greek for ‘twin’).
- It is a suicide mission and the spacecraft will be completely destroyed.

Dimorphos | What is Dimorphos
Dimorphos is a smaller asteroid that revolves around a larger asteroid called Didymos. The DART mission has changed the orbital period of Dimorphos to ensure that they remain in their tight orbit. The European space agency will send the Hera probe to Dimorphos in 2024 in order to ensure that the moonlet is following its intended path.
Reason for choosing Dimorphos ?
- The goal of the mission is to determine how much DART’s impact alters the moonlet’s velocity in space by measuring the change in its orbit around Didymos.
- Scientists think the collision will change the speed of Dimorphos by a fraction of one percent.
- It should alter the moonlet’s orbital period around the larger asteroid by several minutes – enough to be observed and measured by telescopes on Earth.
Asteroids definition | What are asteroids
Asteroids are the belt of rocky particles that revolve around the sun, like planets. Though, they revolve around the sun like planets, they are much smaller than the planets. There are a large number of asteroids found in our solar system but a large number of such asteroids are concentrated in a region between Mars and Jupiter, called the Asteroid Belt. Sometimes, these asteroids leave their path and come within the gravitational force of the Earth and thus become potential threats to the people on the Earth.

Double Asteroid Redirection Test ( DART)
ALSO READ : Web 3.0 : The new generation web
ALSO READ : How to start learning coding